KubeLB is an elastically scalable load balancer with a distributed data plane that can span, serve, and scale with apps across various on-premise and cloud locations. The distributed data plane empowers customers to obtain application affinity at the application microservice levels, thus significantly enhancing the overall application performance. In addition, the clean separation of planes also enables the creation of a unified, centralized control plane that significantly alleviates the operational complexity associated with integrating, operating, and managing each ADC appliance across locations individually.
Terminology
In this chapter, you will find the following KubeLB specific terms:
- Management Cluster/Load Balancing Cluster – A Kubernetes cluster which is responsible for management of all the tenants and their data plane components. Requests for Layer 4 load balancer services are handled by the management cluster.
- Tenant Cluster – A Kubernetes cluster which acts as a consumer of the load balancer services. Workloads that need Layer 4 load balancing are created in the tenant cluster. The tenant cluster hosts the KubeLB Cloud Controller Manager (CCM) component which is responsible for propagating the load balancer configurations to the management cluster.
Design and Architecture
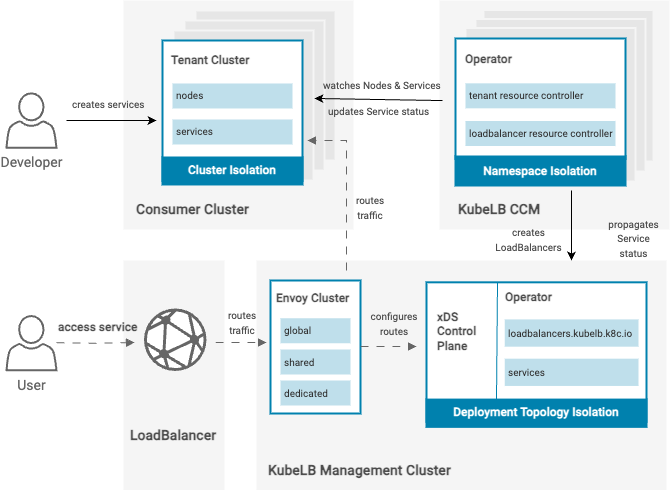
Components
KubeLB comprises of two components:
Cloud Controller Manager
The KubeLB CCM is deployed in the tenant clusters that require load balancer services. Its main responsibility is to propagate the load balancer configurations to the manager.
It watches for changes in Kubernetes services, and nodes, and then generates the load balancer configuration for the manager. It then sends the configuration to the manager in the form of LoadBalancer CRD.
Manager
The KubeLB manager is responsible for deploying and configuring the actual load balancers. The manager registers the tenant clusters as tenants, and then it receives the load balancer configurations from the CCM(s) in the form of LoadBalancer CRD. It then deploys a load balancer and configures it according to the desired specification.
At its core, the KubeLB manager relies on envoy proxy to load balance the traffic. The manager is responsible for deploying the envoy proxy and configuring it for each load balancer service per tenant, based on the envoy proxy deployment topology.
Envoy Proxy Deployment Topology
KubeLB manager supports three different deployment topologies for envoy proxy:
- Shared (default): In this topology, a single envoy proxy is deployed per tenant cluster. All load balancer services in a particular tenant cluster are configured to use this envoy proxy. This is the default topology.
- Dedicated: In this topology, the envoy proxy is deployed per load balancer service.
- Global: In this topology, a single envoy proxy is deployed per KubeLB manager. All load balancer services in all tenant clusters are configured to use this envoy proxy.
Installation
See the installation documentation for more details on how to how to setup and install KubeLB.